Since your app is running on user device, it is quite possible that your ApiKey/SecretKey can be used by untrustworthy user of your app and can be misused. App42 platform offers different way of securing your app however it totally depends on application type and its data. Here are the two main technique to apply ACL on user data and method level calls. If still have concern about security, please feel free to write us at support@shephertz.com and we will surely address it.
Primary requirement with ACL enablement is to have your user registered with App42 platform.
Here are the few steps to apply ACL on your app data.
In ACL enabled app, it is required to pass sessionId of user who is making call. Session Id is used on the server to determine the user and checking for authorization. Session Id can be fetched once user is authenticated as shown below. It uses method call updateEmail for user, however it can be replaced with any other user API call and mechanism will remain same.
If you are using facebook for user integration, you have to pass facebook access token in your API call instead of sessionId. In this case you dont have to call authenticate method as your user authentication is done with facebook.
ServiceAPI serviceAPI = new ServiceAPI("<YOUR_API_KEY>","<YOUR_SECRET_KEY>"); UserService userService = serviceAPI.buildUserService(); User user = userService.authenticate("Nick", "********"); //You can call above method in async mode too by passing call back in overloaded method // Now call any method for example Update Email. This will require Session Id to be passed along with userService.setSessionId(user.getSessionId()); //call setFbAccessToken instead of setSessionId if you are integrating with facebook for user base. User updateUserObj = userService.updateEmail("Nick","nick@shephertz.co.in");Coming SoonServiceAPI serviceAPI = new ServiceAPI("<YOUR_API_KEY>","<YOUR_SECRET_KEY>"); bool flag = true; UserService userService = serviceAPI.BuildUserService(); userService.Authenticate("Nick", "********",new Callback()); public class Callback : App42Callback { public void OnSuccess(Object response) { if (flag) { User user = (User)response; userService.SetSessionId(user.GetSessionId()); //call setFbAccessToken instead of setSessionId if you are integrating with facebook for user base. userService.UpdateEmail("Nick","nick@shephertz.co.in",this); flag = false; //This is to prevent infinite looping of callback } else { User user = (User)response; Console.WriteLine("response is : " + user.ToString()); } } public void OnException(App42Exception exception) { Console.WriteLine("Exception Message " + exception); } }ServiceAPI serviceAPI = new ServiceAPI("<YOUR_API_KEY>","<YOUR_SECRET_KEY>"); UserService userService = serviceAPI.buildUserService(); User user = userService.authenticate("Nick", "********"); // Now call any method for example Update Email. This will require Session Id to be passed along with userService.setSessionId(user.getSessionId()); User updateUserObj = userService.updateEmail("Nick","nick@shephertz.co.in");App42.initialize("<YOUR_API_KEY>","<YOUR_SECRET_KEY>"); var userService = new App42User(); var result ; var updateResult ; userService.authenticate("Nick", "********",{ success: function(object) { var userObj = JSON.parse(object); result = userObj.app42.response.users.user; userService.setSessionId(userObj.getSessiomId()); //call setFbAccessToken instead of setSessionId if you are integrating with facebook for user base. userService.updateEmail("Nick","nick@shephertz.co.in",{ success: function(object) { var updateObj = JSON.parse(object); updateResult = updateObj.app42.response.users.user; console.log("userName is : " + updateResult.userName); }, error: function(error) { } }); }, error: function(error) { } });ServiceAPI serviceAPI = new ServiceAPI("<YOUR_API_KEY>","<YOUR_SECRET_KEY>"); UserService userService = serviceAPI.buildUserService(); User user = userService.authenticate("Nick", "********"); // Now call any method for example Update Email. This will require Session Id to be passed along with userService.setSessionId(user.getSessionId()); //call setFbAccessToken instead of setSessionId if you are integrating with facebook for user base. User updateUserObj = userService.updateEmail("Nick","nick@shephertz.co.in");ServiceAPI serviceAPI = new ServiceAPI("<YOUR_API_KEY>","<YOUR_SECRET_KEY>"); bool flag = true; UserService userService = serviceAPI.BuildUserService(); userService.Authenticate("Nick", "********",new UnityCallBack()); public class UnityCallBack : App42CallBack { public void OnSuccess(object response) { if (flag) { User user = (User)response; userService.SetSessionId(user.GetSessionId()); //call SetFbAccessToken instead of SetSessionId if you are integrating with facebook for user base. userService.UpdateEmail("Nick","nick@shephertz.co.in", new UnityCallBack()); flag = false; //This is to prevent infinite looping of callback } else { User user = (User)response; Console.WriteLine("response is : " + user.ToString()); } } public void OnException(Exception e) { App42Log.Console("Exception : " + e); } }ServiceAPI serviceAPI = new ServiceAPI("<YOUR_API_KEY>","<YOUR_SECRET_KEY>"); UserService userService = serviceAPI.BuildUserService(); User user = userService.Authenticate("Nick", "********"); // Now call any method for example Update Email. This will require Session Id to be passed along with userService.SetSessionId(user.GetSessionId()); //call SetFbAccessToken instead of SetSessionId if you are integrating with facebook for user base. User updateUserObj = userService.UpdateEmail("Nick","nick@shephertz.co.in");Coming SoonComing SoonComing SoonComing Soon
Your admin key of app has got privilege to create/modify/delete data of your app user and app data as well. You have to pass AdminKey in the API call to give it administrative privilege as shown below.
ServiceAPI serviceAPI = new ServiceAPI("<YOUR_API_KEY>","<YOUR_SECRET_KEY>"); UserService userService = serviceAPI.buildUserService(); // Now call any method for example Update Email. Passing admin key will give this administrative privileges. userService.setAdminKey("<Enter_your_admin_key>"); User updateUserObj = userService.updateEmail("Nick","nick@shephertz.co.in"); //You can call above method in async mode too by passing call back in overloaded methodComing SoonServiceAPI serviceAPI = new ServiceAPI("<YOUR_API_KEY>","<YOUR_SECRET_KEY>"); bool flag = true; UserService userService = serviceAPI.BuildUserService(); userService.SetAdminKey("<Enter_your_admin_key>"); userService.UpdateEmail("Nick","nick@shephertz.co.in",new Callback()); public class Callback : App42Callback { public void OnSuccess(Object response) { User user = (User)response; Console.WriteLine("response is : " + user.ToString()); Console.WriteLine("userName is : " + user.GetUserName()); } public void OnException(App42Exception exception) { Console.WriteLine("Exception Message " + exception); } }ServiceAPI serviceAPI = new ServiceAPI("<YOUR_API_KEY>","<YOUR_SECRET_KEY>"); UserService userService = serviceAPI.buildUserService(); // Now call any method for example Update Email. Passing admin key will give this administrative privileges. userService.setAdminKey("<Enter_your_admin_key>"); User updateUserObj = userService.updateEmail("Nick","nick@shephertz.co.in");App42.initialize("<YOUR_API_KEY>","<YOUR_SECRET_KEY>"); var userService = new App42User(); var result ; var updateResult ; userService.authenticate("Nick", "********",{ success: function(object) { var userObj = JSON.parse(object); result = userObj.app42.response.users.user; userService.setAdminKey("<Enter_your_admin_key>"); userService.updateEmail("Nick","nick@shephertz.co.in",{ success: function(object) { var updateObj = JSON.parse(object); updateResult = updateObj.app42.response.users.user; console.log("userName is : " + updateResult.userName); }, error: function(error) { } }); }, error: function(error) { } });ServiceAPI serviceAPI = new ServiceAPI("<YOUR_API_KEY>","<YOUR_SECRET_KEY>"); UserService userService = serviceAPI.buildUserService(); // Now call any method for example Update Email. Passing admin key will give this administrative privileges. userService.setAdminKey("<Enter_your_admin_key>"); User updateUserObj = userService.updateEmail("Nick","nick@shephertz.co.in");ServiceAPI serviceAPI = new ServiceAPI("<YOUR_API_KEY>","<YOUR_SECRET_KEY>"); bool flag = true; UserService userService = serviceAPI.BuildUserService(); userService.SetAdminKey("<Enter_your_admin_key>"); userService.UpdateEmail("Nick","nick@shephertz.co.in", new UnityCallBack() ); public class UnityCallBack : App42CallBack { public void OnSuccess(object response) { User user = (User)response; App42Log.Console("response is : " + user.ToString()); App42Log.Console("userName is : " + user.GetUserName()); } public void OnException(Exception e) { App42Log.Console("Exception : " + e); } }ServiceAPI serviceAPI = new ServiceAPI("<YOUR_API_KEY>","<YOUR_SECRET_KEY>"); UserService userService = serviceAPI.BuildUserService(); // Now call any method for example Update Email. Passing admin key will give this administrative privileges. userService.SetAdminKey("<Enter_your_admin_key>"); User updateUserObj = userService.UpdateEmail("Nick","nick@shephertz.co.in");Coming SoonComing SoonComing SoonComing Soon
Granting Access on given resource or document can be done by using grantAccess method available in respective service. Here is a snippet to grant permission to given user on JSON object stored in specific db and collection.
String dbName = "dbName"; String collectionName = "collectionName"; String objectId = "objectId"; HashSet<ACL> aclList = new HashSet<ACL>(); aclList.add(new ACL("Nick", Permission.READ)); Storage storage = storageService.grantAccessOnDoc(dbName,collectionName,objectId,aclList); //You can call above method in async mode too by passing call back in overloaded method System.out.println("dbName is " + storage.getDbName()); String jsonResponse = storage.toString();Coming SoonString dbName = "dbName"; String collectionName = "collectionName"; String objectId = "objectId"; HashSet<ACL> aclList = new HashSet<ACL>(); aclList.Add(new ACL("John", Permission.READ)); storageService.GrantAccessOnDoc(dbName, collectionName,objectId, aclList, new Callback()); public class Callback : App42Callback { public void OnException(App42Exception exception) { Console.WriteLine("Exception Message"); } public void OnSuccess(Object response) { Storage storage = (Storage) response; String jsonResponse = storage.ToString(); } }String dbName = "dbName"; String collectionName = "collectionName"; String objectId = "objectId"; Hashtable aclList = new Hashtable(); aclList.put("Accessing User", ACL.PERMISSION_READ); Storage storage = storageService.grantAccessOnDoc(dbName,collectionName,objectId,aclList); System.out.println("dbName is " + storage.getDbName()); String jsonResponse = storage.toString();var dbName = "dbName", collectionName = "collectionName", response , objectId = "objectId"; var aclList = new Array(); var acl={ user:"Accessing User", permission:Permission.READ, }; aclList.push(acl) storageService.grantAccessOnDoc(dbName,collectionName,objectId,aclList{ success: function(object) { var storageObj = JSON.parse(object); response = storageObj.app42.response.storage; console.log("dbName is " + response.dbName) }, error: function(error) { } });String dbName = "dbName"; String collectionName = "collectionName"; String objectId = "objectId"; HashSet<ACL> aclList = new HashSet<ACL>(); aclList.add(new ACL("Accesss User", Permission.READ)); Storage storage = storageService.grantAccessOnDoc(dbName,collectionName,objectId,aclList); System.out.println("dbName is " + storage.getDbName()); String jsonResponse = storage.toString();String dbName = "dbName"; String collectionName = "collectionName"; String docId = "objectId"; HashSet<ACL> aclSet = new HashSet<ACL>(); aclSet.Add(new ACL("Nick", Permission.READ)); App42Log.SetDebug(true); //Print output in your editor console storageService.GrantAccessOnDoc(dbName, collectionName, docId, aclSet, new UnityCallBack()); public class UnityCallBack : App42CallBack { public void OnSuccess(object response) { Storage storage = (Storage) response; IList<Storage.JSONDocument> jsonDocList = storage.GetJsonDocList(); for(int i=0;i <jsonDocList.Count;i++) { App42Log.Console("objectId is " + jsonDocList[i].GetDocId()); App42Log.Console("jsonDoc is " + jsonDocList[i].GetJsonDoc()); } } public void OnException(Exception e) { App42Log.Console("Exception : " + e); } }String dbName = "dbName"; String collectionName = "collectionName"; String objectId = "objectId"; HashSet<ACL> aclList = new HashSet<ACL>(); aclList.Add(new ACL("Accesss User", Permission.READ)); Storage storage = storageService.GrantAccessOnDoc(dbName, collectionName,objectId, aclList); Console.WriteLine("dbName is " + storage.GetDbName()); String jsonResponse = storage.ToString();$dbName = "dbName"; $collectionName = "collectionName"; $objectId = "objectId"; $aclList = array(); array_push($aclList, new ACL("Accessing User", Permission::READ)); $storage = $storageService->grantAccessOnDoc($dbName,$collectionName,$objectId,$aclList); print_r("dbName is " . $storage->getDbName()); $jsonResponse = $storage->toString();Coming SoonComing SoonComing Soon
Once Access is given on specific object/resource, you can revoke that access by calling revokeAccess method available in respective service. Here is a snippet to revoke access on given JSON object from user
String dbName = "dbName"; String collectionName = "collectionName"; String objectId = "objectId"; HashSet<ACL> aclList = new HashSet<ACL>(); aclList.add(new ACL("Nick", Permission.READ)); Storage storage = storageService.revokeAccessOnDoc(dbName,collectionName,objectId,aclList); //You can call above method in async mode too by passing call back in overloaded method System.out.println("dbName is " + storage.getDbName()); String jsonResponse = storage.toString();Coming SoonString dbName = "dbName"; String collectionName = "collectionName"; String objectId = "objectId"; HashSet<ACL> aclList = new HashSet<ACL>(); aclList.Add(new ACL("Revoked User", Permission.READ)); storageService.RevokeAccessOnDoc(dbName, collectionName,objectId, aclList,new Callback()); public class Callback : App42Callback { void App42Callback.OnException(App42Exception exception) { Console.WriteLine("Exception Message"); } void App42Callback.OnSuccess(Object response) { Storage storage = (Storage) response; String jsonResponse = storage.ToString(); } }String dbName = "dbName"; String collectionName = "collectionName"; String objectId = "objectId"; Hashtable aclList = new Hashtable(); aclList.put("Revoked User", ACL.PERMISSION_READ); Storage storage = storageService.revokeAccessOnDoc(dbName,collectionName,objectId,aclList); System.out.println("dbName is " + storage.getDbName()); String jsonResponse = storage.toString();var dbName = "dbName", collectionName = "collectionName", response , objectId = "objectId"; var aclList = new Array(); var acl={ user:"Revoked User", permission:Permission.READ, }; aclList.push(acl) storageService.revokeAccessOnDoc(dbName,collectionName,objectId,aclList{ success: function(object) { var storageObj = JSON.parse(object); response = storageObj.app42.response.storage; console.log("dbName is " + response.dbName) }, error: function(error) { } });String dbName = "dbName"; String collectionName = "collectionName"; String objectId = "objectId"; HashSet<ACL> aclList = new HashSet<ACL>(); aclList.add(new ACL("Revoked User", Permission.READ)); Storage storage = storageService.revokeAccessOnDoc(dbName,collectionName,objectId,aclList); System.out.println("dbName is " + storage.getDbName()); String jsonResponse = storage.toString();String dbName = "dbName"; String collectionName = "collectionName"; String docId = "objectId"; HashSet<ACL> aclSet = new HashSet<ACL>(); aclSet.Add(new ACL("Nick", Permission.READ)); App42Log.SetDebug(true); //Print output in your editor console storageService.RevokeAccessOnDoc(dbName, collectionName, docId, aclSet, new UnityCallBack()); public class UnityCallBack : App42CallBack { public void OnSuccess(object response) { Storage storage = (Storage) response; IList<Storage.JSONDocument> jsonDocList = storage.GetJsonDocList(); for(int i=0;i <jsonDocList.Count;i++) { App42Log.Console("objectId is " + jsonDocList[i].GetDocId()); App42Log.Console("jsonDoc is " + jsonDocList[i].GetJsonDoc()); } } public void OnException(Exception e) { App42Log.Console("Exception : " + e); } }String dbName = "dbName"; String collectionName = "collectionName"; String objectId = "objectId"; HashSet<ACL> aclList = new HashSet<ACL>(); aclList.Add(new ACL("Revoked User", Permission.READ)); Storage storage = storageService.RevokeAccessOnDoc(dbName, collectionName,objectId, aclList); Console.WriteLine("dbName is " + storage.GetDbName()); String jsonResponse = storage.ToString();$dbName = "dbName"; $collectionName = "collectionName"; $objectId = "objectId"; $aclList = array(); array_push($aclList, new ACL("Revoked User", Permission::READ)); $storage = $storageService->revokeAccessOnDoc($dbName,$collectionName,$objectId,$aclList); print_r("dbName is " . $storage->getDbName()); $jsonResponse = $storage->toString();Coming SoonComing SoonComing Soon
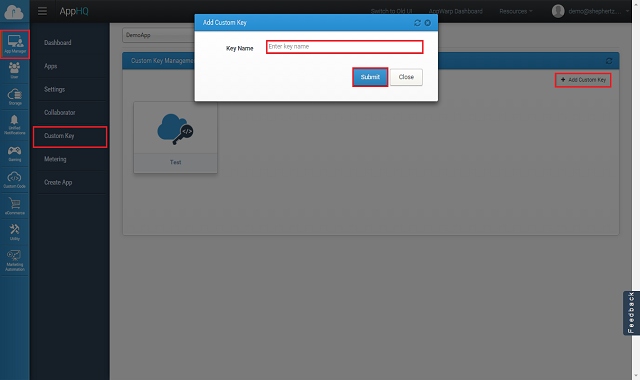
App42 provides hundred of ready made methods that can be used from your app. Since your ApiKey/SecretKey is distributed with App, it is quite possible that any potential hacker can see your ApiKey/SecretKey inside your app and can make a call to all of the APIs available in App42. You can very well handle this scenario by creating separate key for your app and only giving access to required API methods to it. For example, you can create a separate ApiKey which will only have access to create user and authenticate user method of App42 APIs. Rest of the method will not be accessible to this ApiKey.
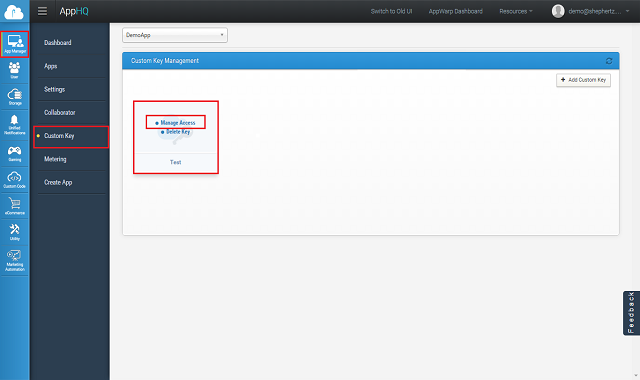
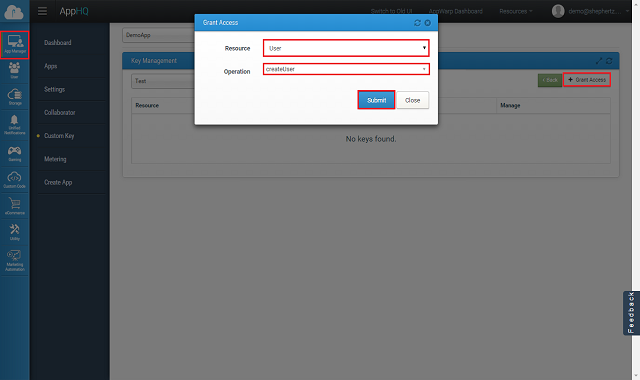
Here are the few steps to create new custom ApiKey and giving method access to it.